Business Intelligence
Written By: Sajagan Thirugnanam and Austin Levine
Last Updated on November 1, 2024
Introduction
Operational reporting is a crucial aspect of business intelligence that focuses on the day-to-day activities of an organization. It provides real-time insights into operational performance, enabling businesses to monitor their processes, make informed decisions, and respond quickly to emerging issues.
This blog post will dive into the definition of operational reporting, its importance, key components, types of reports, and best practices for creating effective operational reports.
What is Operational Reporting
Operational reporting refers to the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and presenting data related to an organization’s daily operations. These reports are designed to provide immediate insights into business processes, allowing stakeholders to track performance metrics and make timely decisions. Unlike strategic reporting, which focuses on long-term goals and trends, operational reporting emphasizes current performance and operational efficiency.
Importance of Operational Reporting
Operational reporting is vital for several reasons:
Real-Time Decision-Making: It enables organizations to respond swiftly to operational challenges by providing up-to-date information.
Actionable Insights: Operational reports deliver insights that can drive improvements in processes and enhance overall efficiency.
Enhanced Collaboration: By providing shared access to critical data, operational reporting fosters collaboration across departments.
Performance Monitoring: Regular operational reports help organizations track their performance against established KPIs.
For example, a retail company can use operational reports to monitor inventory levels in real time, helping them avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
Distinction Between Operational and Strategic Reporting
While both operational and strategic reporting are essential for business success, they serve different purposes:
Operational Reporting: Concentrates on current performance metrics and day-to-day operations.
Strategic Reporting: Provides a long-term view of organizational performance against strategic goals.
Examples of Operational Reporting in Business Contexts
Operational reporting can be applied across various industries:
Retail Inventory Tracking: Retailers use operational reports to monitor stock levels and sales trends in real-time.
Manufacturing Workflow Optimization: Manufacturers analyze production data to identify bottlenecks and improve efficiency.
Sales Performance Monitoring: Sales teams utilize operational reports to track daily sales activities and conversion rates.
Key Components of an Effective Operational Report
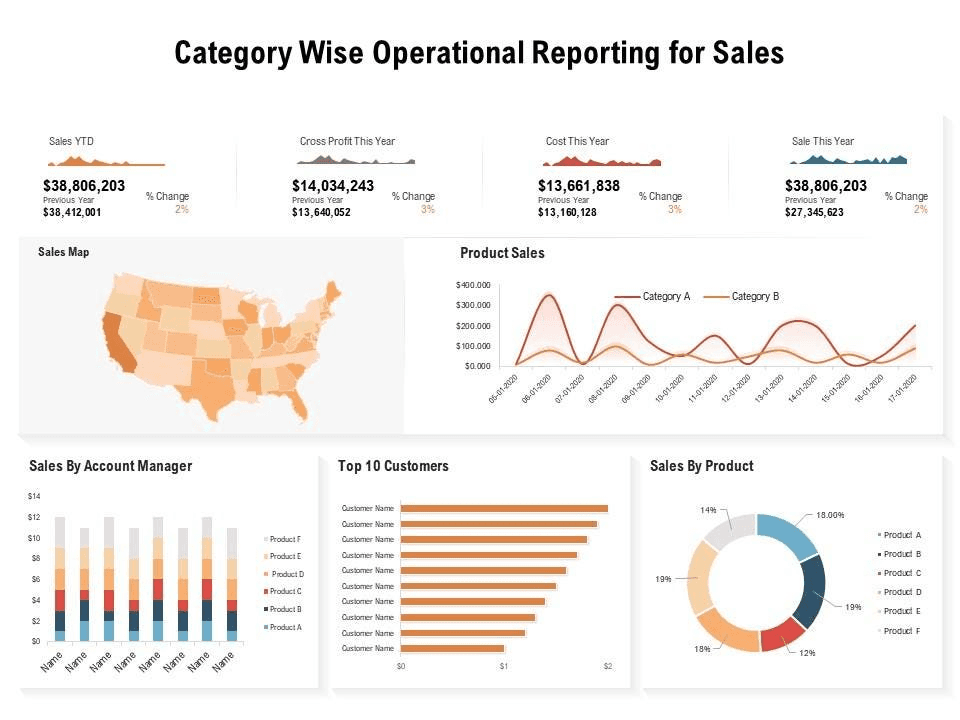
Source: Medium
To create effective operational reports, several key components must be considered:
Data Sources and Real-Time Data Integration
Gathering data from various sources such as CRM systems, ERP platforms, and IoT devices is crucial. Real-time data integration ensures that information is always up-to-date, allowing for accurate reporting.
KPIs and Metrics for Operational Efficiency
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential for measuring operational success. Common metrics include production cycle time, sales per hour, and response times. Selecting the right KPIs tailored to specific business needs is vital for actionable insights.
Visual Elements: Making Data Digestible
Effective visualization techniques—such as charts, tables, and dashboards—are important for presenting data clearly. Well-designed visual elements allow stakeholders to quickly grasp complex information.
Types of Operational Reports
There are several types of operational reports that serve different purposes:
Inventory and Stock Management Reports
These reports monitor inventory levels, turnover rates, and reorder points. They help businesses manage stockouts and overstock scenarios effectively.
Sales and Marketing Performance Reports
These reports track sales volume, conversion rates, and customer acquisition metrics. They provide real-time insights into marketing campaign effectiveness.
Customer Support and Service Level Reports
These reports include customer satisfaction metrics, issue resolution times, and support queue status. They are critical for maintaining quality customer service.
Financial Health Reports
These reports analyze cash flow, and accounts receivable/payable tracking. They provide real-time insights into financial health for operational adjustments.
Operational Efficiency Reports
These reports assess metrics related to production, distribution, and workflow efficiency. They help identify bottlenecks and areas needing improvement.
How to Create Effective Operational Reports
Creating effective operational reports involves several steps:
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Audience
Understanding the report's goals is crucial. Determine who will use the report and for what purpose; tailor content accordingly.
Step 2: Select Relevant KPIs and Metrics
Align KPIs with operational goals to provide actionable insights while avoiding data overload by focusing on key metrics.
Step 3: Gather Real-Time Data and Automate Data Collection
Integrate with tools that allow real-time data access (e.g., Power BI). Automation minimizes manual entry errors.
Step 4: Choose Appropriate Visualizations and Format
Select visualizations that make the data intuitive. Consider layout design for enhanced readability.
Step 5: Test and Refine Reports
Review reports with end-users to ensure clarity; adjust based on feedback for continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Operational Reporting
To enhance the effectiveness of your operational reporting:
Ensure Data Accuracy and Consistency: Implement regular validation processes.
Prioritize Real-Time Data Updates: Ensure timely updates to maintain relevance.
Optimize for Accessibility and Usability: Make reports accessible through mobile or web interfaces.
Automate Reporting Where Possible: Leverage automation tools to reduce manual tasks.
Regularly Review and Update KPIs: Adjust metrics as business needs evolve.
Maintain Data Security and Compliance: Follow best practices for data governance.
Tools and Technologies for Operational Reporting
Several tools can facilitate effective operational reporting:
Power BI: Offers robust visualization capabilities with real-time analytics.
Tableau: Known for its interactive dashboards that provide deep insights into operations.
Looker: Focuses on providing real-time insights through an intuitive interface.
When choosing a reporting tool, consider factors such as integration capabilities with existing systems, user-friendliness, customization options, and support for real-time analytics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, operational reporting is essential for organizations seeking to enhance their decision-making processes based on accurate data insights. By understanding its components—data collection, processing, analysis—and following best practices in report creation, businesses can leverage these insights effectively.
Related to Business Intelligence