Business Intelligence
Written By: Sajagan Thirugnanam and Austin Levine
Last Updated on November 1, 2024
In today's data-driven world, organizations must develop a robust data strategy to leverage their data effectively. A well-structured data strategy not only enhances decision-making but also aligns with business objectives, ensuring that data serves as a valuable asset rather than just a byproduct of operations.
What is a Data Strategy?
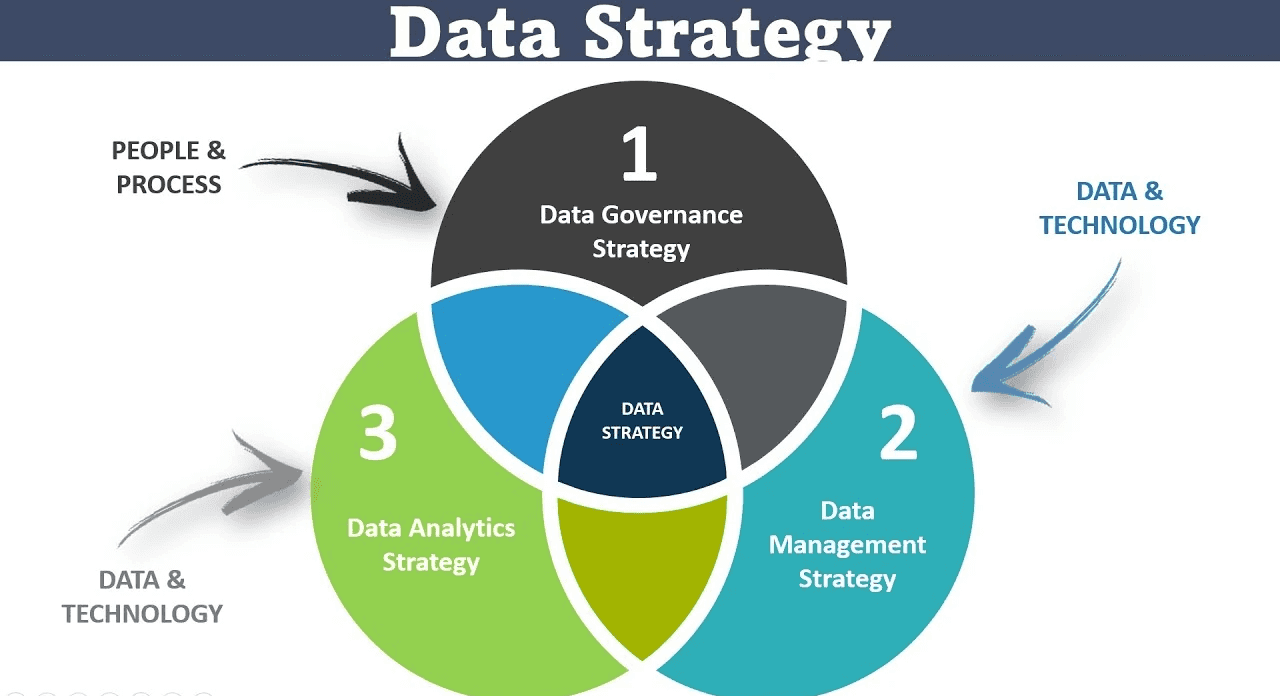
A Data Strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines how an organization will collect, manage, analyze, and utilize data to achieve its business goals. It encompasses the technology, processes, people, and governance needed to optimize data usage across the organization. This strategy is essential for ensuring that data is treated as a strategic asset, enabling better decision-making and operational efficiency.
Data Strategy: What Problem Does It Solve?
The primary challenge that a data strategy addresses is the chaotic and often inefficient management of data within organizations. Without a clear strategy, businesses may struggle with:
Data Silos: Isolated data sets that hinder collaboration and insights.
Inconsistent Data Quality: Variability in data accuracy and reliability can lead to poor decision-making.
Regulatory Compliance Risks: Organizations may fail to meet legal requirements regarding data governance and privacy.
Missed Opportunities for Insights: Without advanced analytics capabilities, companies may overlook valuable trends and insights hidden within their data.
By establishing a clear data strategy, organizations can streamline their data processes, enhance collaboration, and ensure compliance while maximizing the value derived from their data assets.
7 Elements of a Data Strategy
1 of 7: Setting the Vision and Objectives for Data Usage
Establishing a clear vision and specific objectives is fundamental to a successful data strategy.
This involves articulating how data will support business goals and identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success. For instance, a retail company might set an objective to increase customer retention by 15% over the next year through targeted marketing campaigns informed by customer data analysis.
Example: A fictional company, "DataSnacks," aims to enhance customer insights to drive growth. During a workshop, stakeholders define objectives such as improving customer segmentation and personalizing marketing efforts based on data-driven insights. This clarity helps guide all subsequent data initiatives.
2 of 7: Governance and Compliance
Data governance ensures that data management practices are aligned with regulatory requirements and organizational policies.
This includes defining roles, responsibilities, and processes for data stewardship, as well as establishing protocols for data access and usage. A strong governance framework not only protects sensitive information but also enhances trust in data across the organization.
Example: A financial institution implements strict governance policies to comply with regulations like GDPR. They establish a data governance committee responsible for overseeing data quality, access controls, and compliance audits, ensuring that all departments adhere to these standards.
3 of 7: Data Architecture
Data architecture refers to the structured framework that dictates how data is collected, stored, processed, and accessed. A well-defined architecture supports efficient data flows and integration across various systems. It encompasses databases, data warehouses, and cloud storage solutions that facilitate seamless access to information.
Example: A healthcare provider designs its data architecture to integrate patient records from multiple sources into a centralized cloud-based system. This architecture allows healthcare professionals to access comprehensive patient histories quickly, improving care coordination and decision-making.
4 of 7: Data Quality and Accessibility
High-quality data is crucial for reliable analysis and decision-making. Organizations must implement processes to ensure that their data is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. Additionally, making data accessible to authorized users fosters collaboration and empowers employees to leverage insights effectively.
Example: An e-commerce platform conducts regular audits of its product database to remove duplicates and outdated entries. By ensuring high data quality and providing easy access through user-friendly dashboards, the company enables its marketing team to create effective campaigns based on accurate product information.
5 of 7: Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI)
Incorporating advanced analytics capabilities allows organizations to extract deeper insights from their data. This includes leveraging machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics or utilizing BI tools for real-time reporting. Such capabilities enable businesses to make proactive decisions based on trends and patterns identified in their data.
Example: A manufacturing company uses predictive analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur. By analyzing historical maintenance records and sensor data from machinery, they can schedule preventative maintenance, reducing downtime and saving costs.
6 of 7: Data Security
With increasing threats related to cyberattacks and data breaches, implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting sensitive information. This includes encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits to safeguard against unauthorized access or data loss.
Example: A tech startup adopts a multi-layered security approach by implementing encryption for sensitive customer data both at rest and in transit. They also conduct regular employee training on security best practices to minimize the risk of phishing attacks.
7 of 7: Culture of Data Literacy
Fostering a culture of data literacy within an organization ensures that employees at all levels understand how to effectively work with data.
This involves providing training programs that enhance skills in data analysis, interpretation, and visualization. Encouraging curiosity about data can lead to innovative solutions and improved decision-making across the organization.
Example: A large retail chain launches a "data champions" program where select employees receive advanced training in analytics tools. These champions then mentor their colleagues, promoting a culture where employees feel empowered to use data in their daily roles, leading to more informed business decisions.
By addressing these seven elements comprehensively, organizations can build a robust data strategy that not only supports their current needs but also adapts as they grow and evolve in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
How It Affects A Business Without Any Data Strategy
Businesses lacking a cohesive data strategy often face significant challenges:
Inefficiencies in operations due to disorganized or inaccessible data.
Poor decision-making stemming from unreliable or incomplete information.
Increased risk of non-compliance with regulatory standards.
Missed opportunities for innovation due to inadequate insights from available data.
Without a structured approach to managing their data assets, organizations may struggle to remain competitive in an increasingly analytics-driven marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of a successful data strategy?
Key components include vision setting, governance, architecture, quality assurance, advanced analytics capabilities, security measures, and fostering a culture of literacy.
How can I assess my organization's current data maturity?
Conducting a maturity assessment involves evaluating existing processes, technologies, governance structures, and employee skills related to data management.
Why is alignment between business strategy and data strategy important?
Alignment ensures that data initiatives directly support organizational goals, maximizing the return on investment in data resources.
Closing Words
Developing an effective data strategy is essential for organizations aiming to harness the full potential of their data. By focusing on the seven critical elements outlined above, businesses can create a roadmap that not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives innovation and growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Related to Business Intelligence