Business Intelligence
Written By: Sajagan Thirugnanam and Austin Levine
Last Updated on November 1, 2024
Introduction
As businesses increasingly navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, a well-crafted cloud migration strategy has become essential for success. Cloud migration involves transferring data, applications, and other business elements from on-premises infrastructure to cloud environments. This transition not only modernizes IT infrastructure but also unlocks a plethora of benefits that can significantly enhance operational efficiency and scalability.
In this blog post, we will explore the critical components of a cloud migration strategy, detailing how it works and the core benefits it provides to businesses. We will also examine various types of migration strategies, outline the phases of a successful migration process, and discuss common challenges organizations face during this transition.
What is A Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration refers to the process of moving digital assets—such as applications, data, and workloads—from on-premises servers or traditional data centers to a cloud computing environment. This shift can be partial or complete, depending on an organization’s needs and goals. The primary aim of cloud migration is to leverage the advantages of cloud computing—such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness—while minimizing disruption to business operations.
Source: LinkedIn
Organizations may choose to migrate to different types of cloud environments, including public clouds (managed by third-party providers like AWS or Microsoft Azure), private clouds (dedicated infrastructure for a single organization), or hybrid clouds (a combination of both). Each type offers unique benefits tailored to specific business requirements.
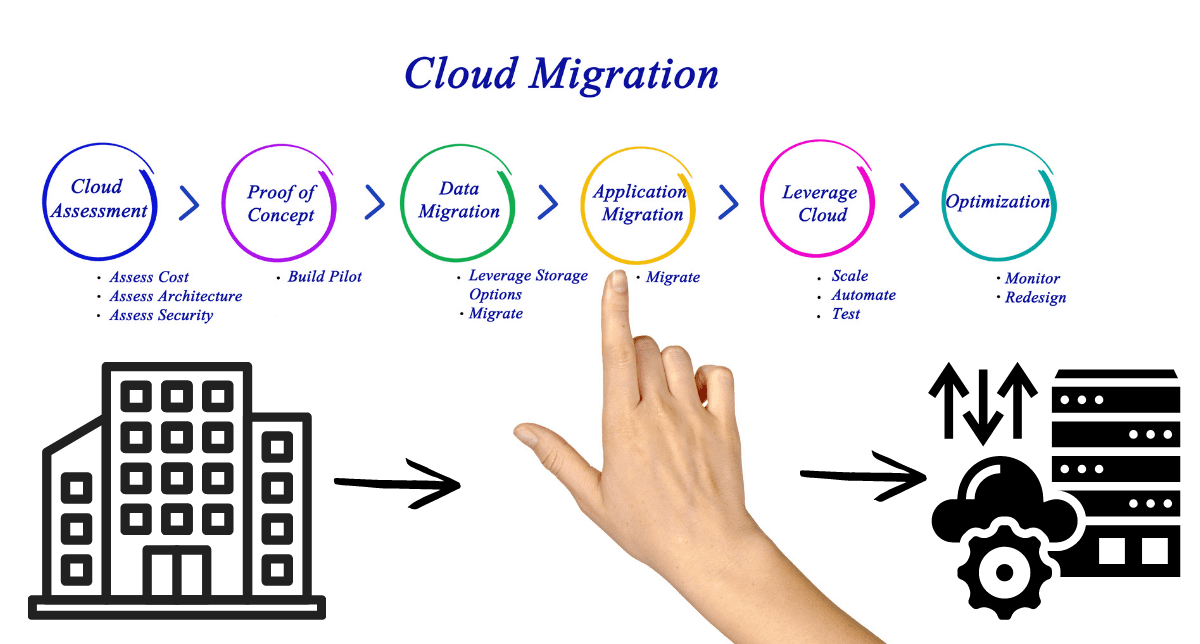
How Does a Cloud Migration Strategy Work?
A cloud migration strategy outlines the approach an organization will take to transition its assets to the cloud. This strategy typically involves several key steps:
Assessment: Evaluating current IT infrastructure and identifying which applications and data are suitable for migration.
Planning: Developing a comprehensive plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and risk management strategies.
Execution: Implementing the migration in phases to minimize disruption and ensure that all systems function correctly in the new environment.
Optimization: Continuously monitoring performance post-migration to ensure that resources are being used efficiently and effectively.
By following a structured approach, organizations can ensure a smoother transition while maximizing the benefits of their new cloud environment.
What are the Core Benefits of Cloud Migration For A Business?
Cloud migration offers numerous advantages that can transform how businesses operate:
Cost Savings: By migrating to the cloud, organizations can reduce capital expenditures associated with maintaining physical infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to only pay for what they use, significantly lowering operational costs.
Scalability: The cloud provides virtually unlimited resources that can be scaled up or down based on demand. This flexibility enables businesses to respond quickly to market changes without overprovisioning hardware.
Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based tools facilitate remote work and improve team collaboration by allowing employees to access data and applications from anywhere.
Improved Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery solutions that enhance business continuity by ensuring quick data recovery in case of disruptions.
Increased Agility: Organizations can deploy applications faster and adapt their IT resources in real-time, improving overall responsiveness to customer needs.
These benefits collectively empower businesses to innovate more rapidly while maintaining operational efficiency.
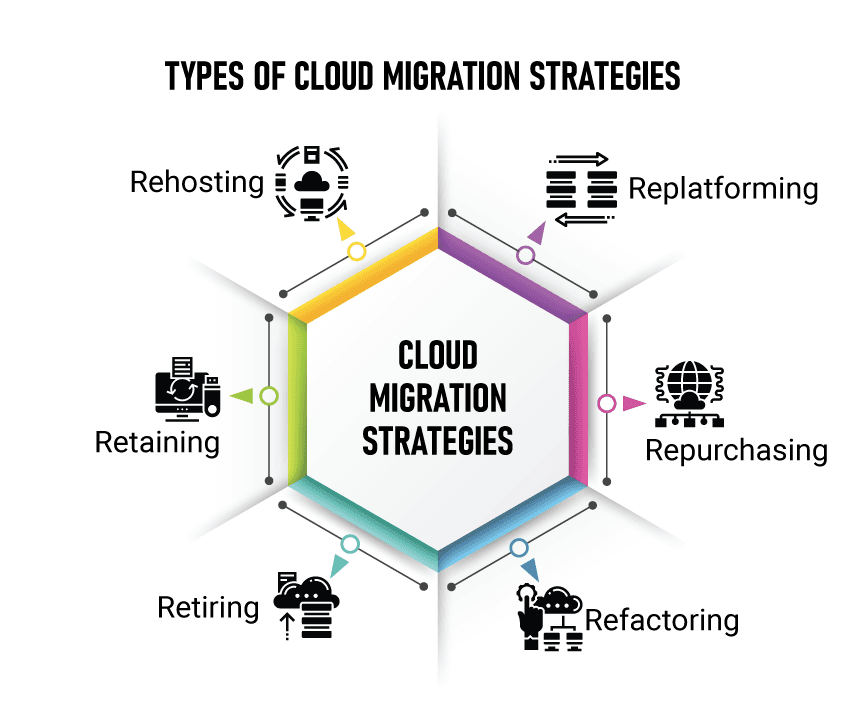
Different Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
Source: LinkedIn
Organizations can choose from several types of cloud migration strategies based on their specific needs:
Relocating
This involves moving existing applications and data directly to the cloud without significant changes. It is often referred to as "lift-and-shift."Reprovision from Scratch
In this strategy, applications are rebuilt in the cloud environment instead of being migrated as-is. This allows for optimization but requires more time and resources.Cold Migration
Cold migration occurs when systems are offline during the transfer process. This approach is typically used for non-critical applications where downtime is acceptable.Live Migration
Live migration allows applications to be moved without downtime. This method is ideal for mission-critical systems that require continuous availability.Replatforming
Replatforming involves making minimal changes to applications before migrating them to take advantage of cloud capabilities while still retaining most of their original architecture.Repurchasing
This strategy entails replacing existing applications with new SaaS solutions that meet similar business needs, often resulting in enhanced functionality.Refactoring
Refactoring involves reworking application code to optimize it for the cloud environment. This can lead to improved performance but requires significant development effort.Retaining
Some applications may be kept on-premises due to compliance or performance requirements while other components are migrated.Retiring
This strategy involves decommissioning outdated applications that are no longer needed or relevant in the new environment.
Decide on the Approach First: Rehost, Refactor or Replatform?
Before initiating a migration project, organizations must decide on their approach—whether they will rehost (lift-and-shift), refactor (make some changes), or replatform (optimize for the cloud). Each approach has its own implications for cost, time, and resource allocation. A thorough assessment of business needs and application requirements will guide this decision-making process.
5 Phases of A Cloud Migration for A Business
A successful cloud migration typically follows five distinct phases:
Phase 1: Preparatory Phase
In this initial phase, organizations assess their current IT landscape, identify key stakeholders, and define objectives for the migration project.
Phase 2: Planning Stage
During planning, businesses develop detailed strategies that outline timelines, budget considerations, resource allocation, and risk management plans.
Phase 3: Migration
This phase involves executing the planned migration activities while ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations. It may include testing applications in the new environment before going live.
Phase 4: Operation
Once migrated, organizations must monitor system performance closely to ensure everything operates smoothly in the new environment.
Phase 5: Optimization
Post-migration optimization focuses on refining processes and configurations based on performance metrics gathered during operation. Continuous improvement ensures that businesses fully leverage their cloud investments.
Challenges To Face During Cloud Migration
Despite its many benefits, organizations may encounter several challenges during cloud migration:
Challenge 1: Cost Management
While cloud migration can reduce costs overall, unexpected expenses may arise if not carefully managed. Organizations must monitor usage closely to avoid overspending.
Challenge 2: Lack of Proper Strategy
Without a well-defined strategy in place, organizations risk misalignment between their business goals and their cloud initiatives. This can lead to inefficient migrations and wasted resources.
Challenge 3: Data Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security during migration is critical. Organizations must address compliance requirements related to data handling and storage throughout the process
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What is cloud migration?
Cloud migration is the process of moving digital assets from on-premises infrastructure to a cloud computing environment.
What are some common challenges faced during cloud migration?
Common challenges include cost management issues, lack of a proper strategy, and concerns about data security and compliance.
What are the benefits of migrating to the cloud?
Benefits include cost savings, scalability, enhanced collaboration capabilities, improved disaster recovery options, and increased agility in operations.
Verdict
Cloud migration represents a transformative opportunity for businesses seeking modernized IT infrastructure that enhances efficiency and competitiveness.
By understanding its core elements—from defining strategies and phases to navigating challenges—organizations can successfully leverage cloud technology's full potential. As digital transformation continues reshaping industries worldwide, adopting a robust cloud migration strategy will be pivotal in achieving sustained growth and innovation in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Related to Business Intelligence