Business Intelligence
Written By: Sajagan Thirugnanam and Austin Levine
Last Updated on November 1, 2024
Introduction
In an age where data is a critical asset for organizations, establishing a robust data governance strategy is essential. This strategy ensures that data is managed effectively, securely, and in compliance with relevant regulations.
A well-defined data governance framework not only enhances data quality but also fosters trust among stakeholders, leading to improved decision-making and operational efficiency. In this blog post, we will outline the seven key steps to building an effective data governance strategy.
What is A Data Governance Strategy?
A data governance strategy is a comprehensive framework that outlines how an organization manages its data assets. It encompasses policies, procedures, roles, and responsibilities that guide the collection, storage, usage, and sharing of data. The primary aim of this strategy is to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance while maximizing the value derived from data across the organization.
Why is a Data Governance Strategy Essential?
A well-implemented data governance strategy is crucial for several reasons:
Improved Data Quality: By establishing clear policies and standards, organizations can enhance the accuracy and consistency of their data.
Regulatory Compliance: A robust governance framework helps organizations comply with legal requirements related to data privacy and security.
Better Decision-Making: Reliable data supports informed decision-making processes across all levels of the organization.
Risk Management: Effective governance reduces the risks associated with data breaches and misuse.
Step 1: Define Data Governance Goals and Objectives
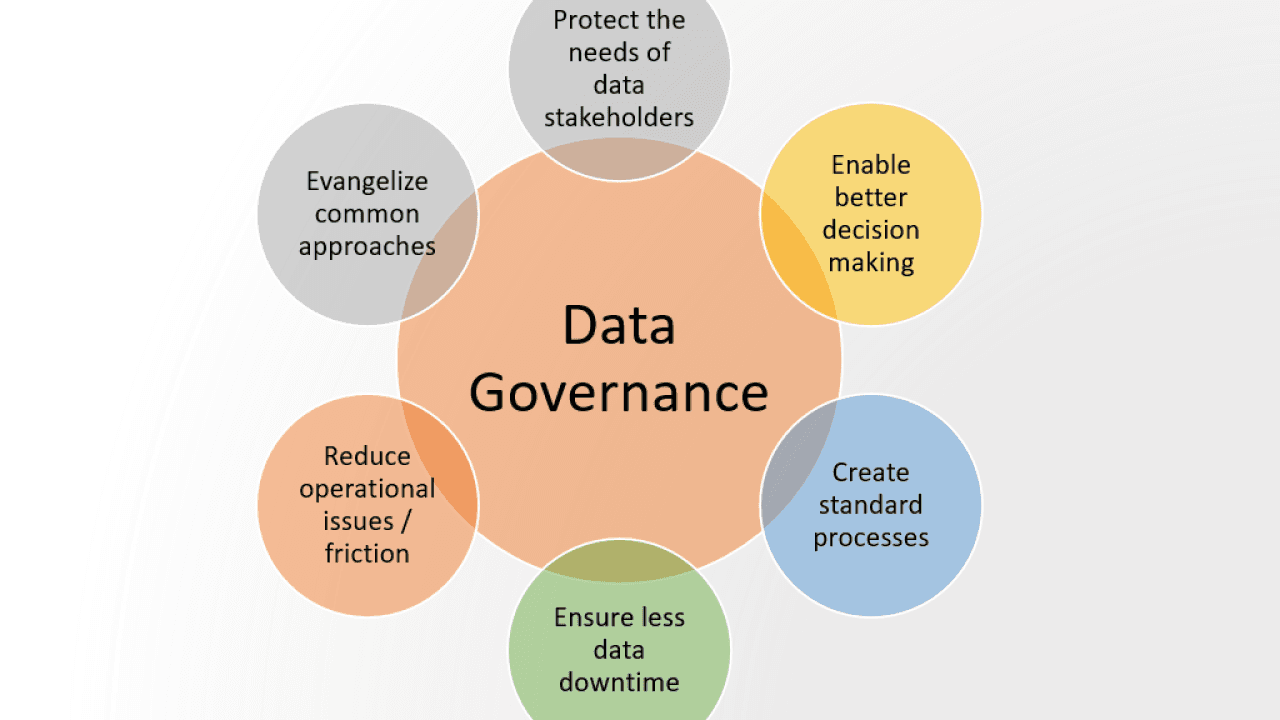
The first step in building a data governance strategy is to clearly define the goals and objectives. This involves identifying what the organization aims to achieve through its data governance efforts. Goals may include improving data quality, ensuring compliance with regulations, or fostering a culture of accountability regarding data usage. Aligning these objectives with broader business goals ensures that the data governance strategy supports overall organizational success.
Step 2: Establish Data Governance Roles and Responsibilities
Once goals are defined, it’s essential to establish clear roles and responsibilities within the organization. This includes appointing a Data Governance Council or committee responsible for overseeing governance initiatives. Key roles might include:
Data Stewards: Individuals responsible for managing specific datasets and ensuring their quality.
Data Owners: Those who have authority over specific datasets and make decisions regarding their usage.
Data Users: Employees who access and utilize data in their daily tasks.
Clearly defined roles help prevent confusion and ensure accountability throughout the organization.
Step 3: Develop Data Policies and Standards
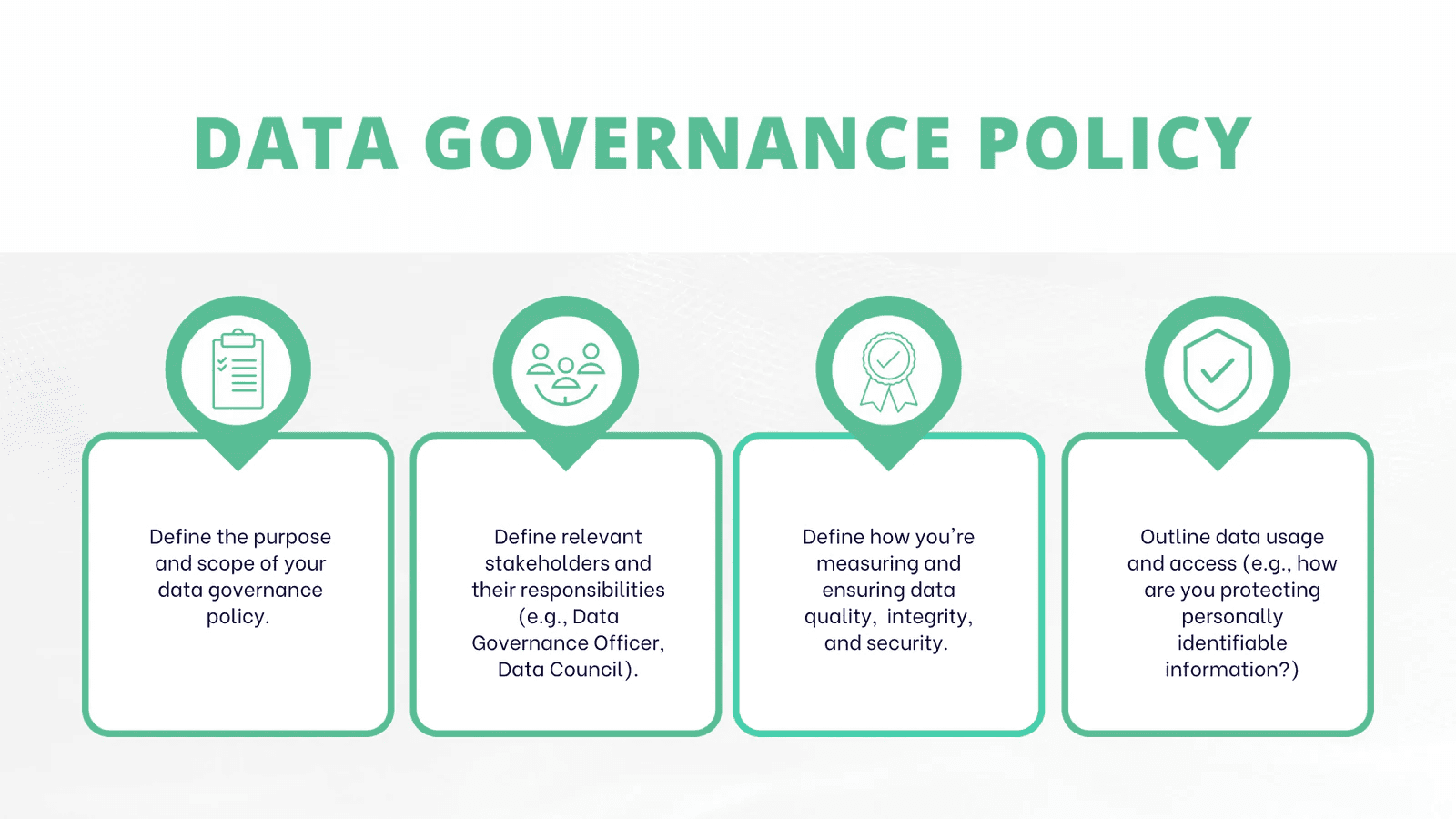
Source: Segment
Developing comprehensive data policies and standards is crucial for effective governance. These policies should outline how data is collected, stored, accessed, and shared within the organization. Standards should address aspects such as:
Data quality metrics
Security protocols
Compliance requirements
By establishing these guidelines, organizations can create a consistent approach to managing their data assets.
Step 4: Design Data Governance Processes and Workflows
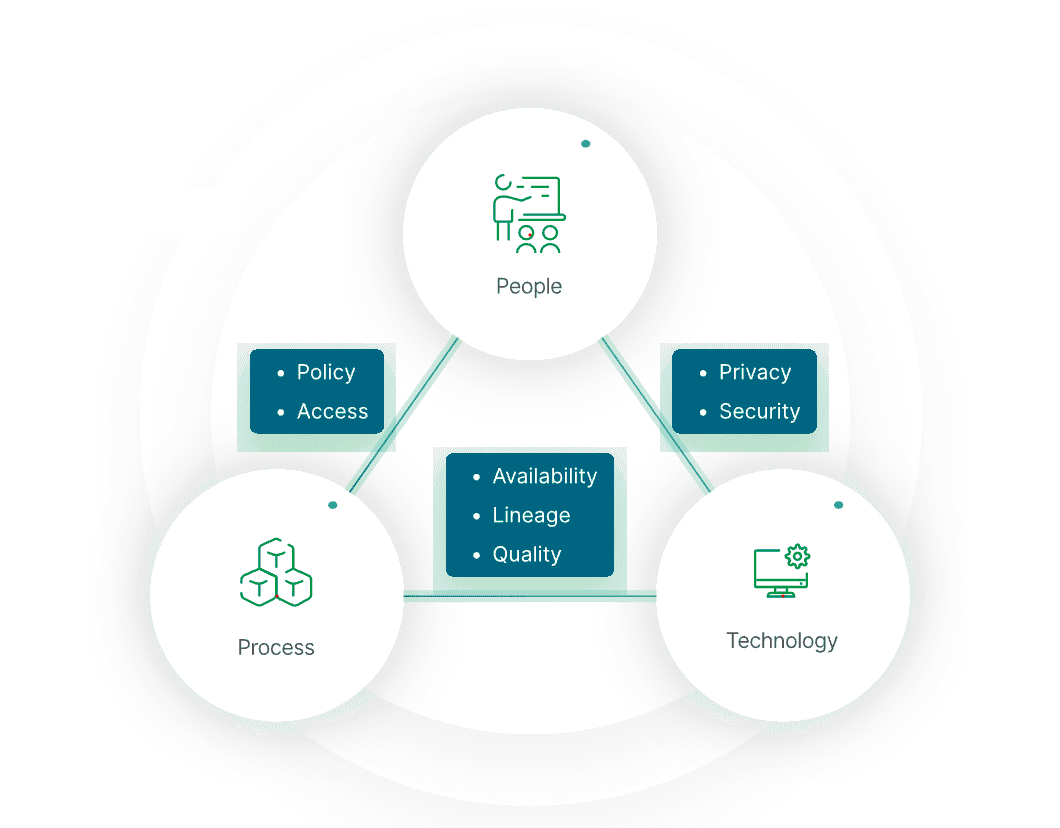
Source: Qlik
Designing processes and workflows for data governance involves outlining how various tasks related to data management will be executed. This includes defining procedures for:
Data entry and validation
Data access requests
Incident reporting for data breaches or quality issues
Well-defined processes ensure that all stakeholders understand their responsibilities and can work effectively within the governance framework.
Step 5: Implement Data Governance Tools and Technology
To support the execution of a data governance strategy, organizations must invest in appropriate tools and technologies. These tools can facilitate:
Data cataloging
Metadata management
Data quality monitoring
Compliance tracking
Selecting the right technology solutions enables organizations to automate processes, enhance collaboration, and maintain oversight of their data assets.
Step 6: Foster a Data-Driven Culture and Promote Data Literacy
Creating a culture that values data-driven decision-making is essential for successful implementation of a governance strategy. Organizations should invest in training programs that promote data literacy among employees. This includes educating staff on:
The importance of data governance
How to use data responsibly
The roles they play in maintaining data integrity
Fostering this culture encourages accountability and empowers employees to leverage data effectively.
Common Challenges in Data Governance and How to Overcome Them
Challenge 1: Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance from employees can hinder the implementation of a new governance framework. To overcome this challenge, organizations should communicate the benefits of governance clearly and involve employees in the development process.
Challenge 2: Balancing Security with Accessibility
Organizations often struggle to balance stringent security measures with the need for easy access to data. Implementing role-based access controls can help ensure that users have access only to the information they need while maintaining security protocols.
Challenge 3: Managing Data Across Multiple Systems
Data may reside in various systems across an organization, complicating governance efforts. Establishing a centralized repository or using integration tools can help streamline access and management of disparate datasets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of a successful data governance strategy?
Key components include defined goals, established roles, comprehensive policies, designed processes, appropriate tools, and a culture of accountability regarding data usage.
How often should a data governance strategy be reviewed?
A review should occur at least annually or whenever significant changes occur within the organization or its regulatory environment.
What role does technology play in data governance?
Technology supports the automation of processes, enhances collaboration among stakeholders, ensures compliance tracking, and improves overall efficiency in managing data assets.
Conclusion
Building a robust data governance strategy is essential for organizations aiming to maximize the value of their data while ensuring compliance with regulations and maintaining high-quality standards.
By following these seven steps—defining goals, establishing roles, developing policies, designing processes, implementing tools, and fostering a culture of literacy—organizations can create an effective framework that enhances decision-making capabilities and drives business success in today’s digital landscape.
Related to Business Intelligence