Power BI Tutorials
Written By: Sajagan Thirugnanam and Austin Levine
Last Updated on October 29, 2024
Power BI, a leading business intelligence platform from Microsoft, provides an array of tools to help organizations analyze data and make informed decisions. One such tool within Power BI that has gained increasing prominence is Dataflows.
Dataflows in Power BI is an advanced feature that enables you to connect and retrieve data from various sources, followed by data transformation using the online Power Query Editor. Dataflows enable the process of extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data more efficiently, offering a robust mechanism for dealing with data at scale, ensuring consistency, and enhancing reusability.
Let us delve deeper into dataflows in Power BI and understand how we can leverage it to improve our Power BI expertise.
What Are Dataflows in Power BI?
At its core, dataflows are a cloud based technology in Power BI feature that facilitates data preparation processes for various reports and dashboards. This feature allows users to create a collection of reusable ETL processes. These processes can extract data from various sources, clean and transform the data, and store it in a common data model or a format that can be shared across multiple Power BI reports and dashboards.
Dataflows have many different connectors and APIs to retrieve data from any supported source out there. To create a dataflow, you would need to be within the Power BI Service platform - you cannot create a dataflow in Power BI from the desktop version of Power BI. However, please note that any dataflow created with the service can be accessed and utilized in the Power BI desktop application to establish connection and get data.
So what exactly are the output elements of a Power BI Dataflow?
Well, to put it simply it is a collection of tables which do not necessarily form a relational model without creating relationships between them, unlike a dataset. Once created, these tables can be called into your reports within Power BI Desktop to create reports and dashboards.
How to Use Dataflows in Power BI
To create a dataflow in Power BI, follow these steps:
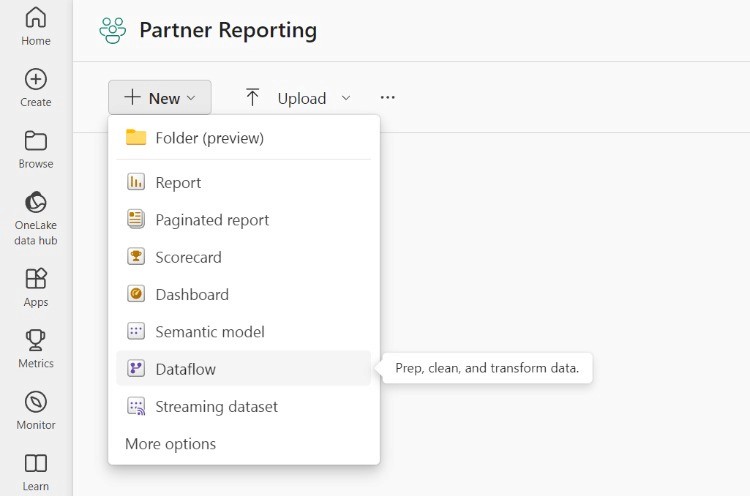
From within Power BI Service, navigate to the workspace where you want the dataflow to be created. Click the New button and select Dataflow from the dropdown menu
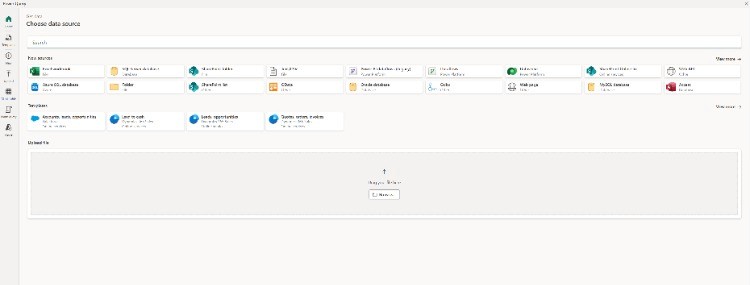
Choose the data source from the list of sources.
After selecting your data source, Power BI provides a Power Query-like experience to clean and transform the data. You can remove unnecessary columns, rename fields, merge tables, apply filters, and more.
So if you already know Power Query, this step should be a breeze for you!
Save the dataflow you just created and schedule refreshes as per your requirement.
Now you can start using the dataflow in your reports from Power BI Desktop. To do this simply click on Get Data from Power BI Desktop and select Power BI Dataflows. From here you can select the dataflow you created and import the data directly into your report.
Key Features of Power BI Dataflows
Dataflows can come in very handy for a number of reasons as you may have already guessed.
Reusable ETL processes: You can create a dataflow once and reuse it across multiple Power BI reports and dashboards.
Support for multiple data sources: Dataflows can pull data from a wide range of data sources, including databases, cloud services, and on-premise systems.
Scheduling and incremental refreshes: With dataflows, you can automate the refresh of data and configure incremental refreshes to improve performance and reduce load on your source systems.
Dataflows vs. Power Query in Power BI Desktop
Well you might be wondering at this point - why use dataflows instead of the native Power Query we are so used to and familiar with.
For starters, dataflows are structured for centralized data transformation enabling us to create reusable data transformations that can be used across several reports by the team unlike Power Query which is basically a data transformation tool within Power BI desktop for that specific report you are creating.
There are other key differences as well to how these two work behind the scenes. Power Query within the desktop application is much faster than dataflows. Moreover, while creating dataflows using the Service platform you might run into situations where all errors are converted to null values - however, in Power Query desktop this would be displayed and indicated.
When to Use Dataflows in Power BI
Power BI offers various tools for working with data, so it’s essential to know when Dataflows are the right choice. Here are key scenarios where Dataflows shine:
When Working with Complex Data Transformations
When You Need Centralized Data Preparation
When You Want to Use a Common Data Model
When Dealing with Large or Incremental Data Loads
When You Need Data Reusability Across Multiple Reports
Conclusion
Power BI Dataflows are a powerful tool that can enhance the way your organization prepares and manages data. By centralizing data preparation, improving reusability, and supporting complex transformations, Dataflows can save time and ensure consistency across reports and teams.
Whether you are completely new to dataflows in Power BI or simply looking to enhance your company’s data infrastructure, you have come to the right place. To gain more in-depth knowledge on Power BI and its related topics, please refer to Case When. They offer amazing services related to Data Engineering, Business Intelligence and Product Analytics.
FAQs
What are the different uses of Dataflows?
To put simply, dataflows are a cloud based technology in Power BI feature that facilitates data preparation processes for various reports and dashboards. This feature allows users to create a collection of reusable ETL processes.
What is Dataflow vs. dataset in Power BI?
Dataflows are a collection of tables which do not necessarily form a relational model without creating relationships between them unlike a dataset. Essentially, dataflows handle the data transformation part and makes the data reusable across multiple reports.
Related to Power BI Tutorials